unconstrainedBootstrapperExample.cpp
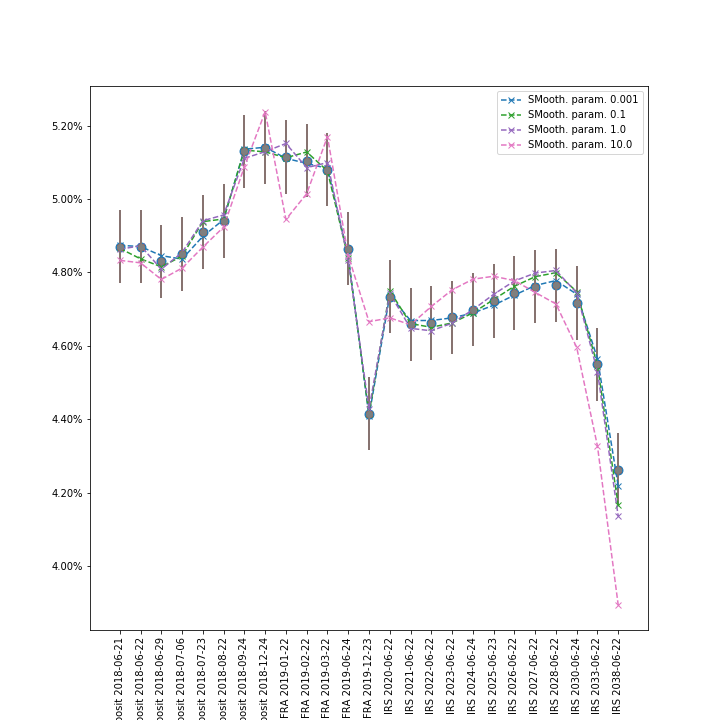
This example show how to build curve using unconstrained bootstrapper (UnconstrainedBootstrapper). Programme uses data files stored as csv in ./data directory Plots below presents the interest rate curves build using different smoothing parameters
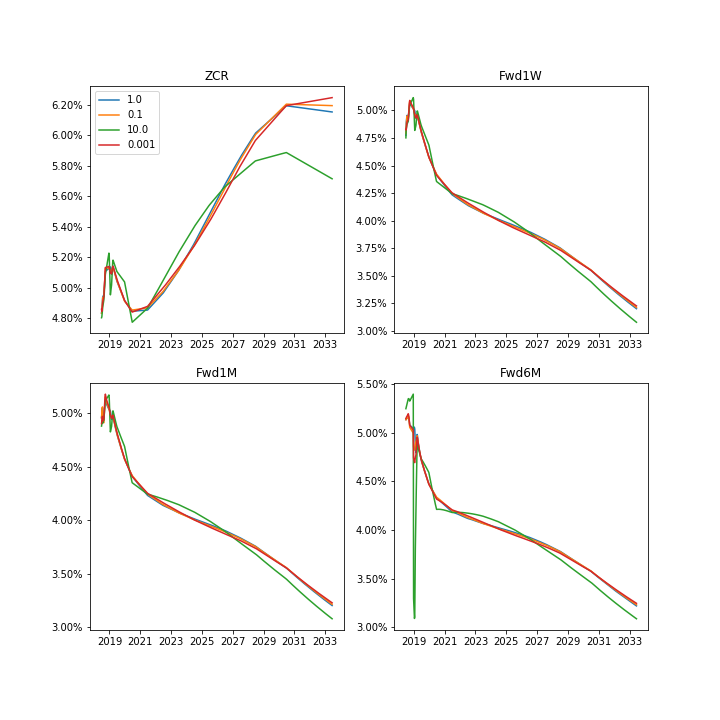
Here we present the calibration of the curve. We see that for larger value of smooth parameters the calibration is worth but curve is smoother.
#include <juliant.hpp>
#include "factoryInit.hpp"
using namespace julian;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
RunTimeMeasurment timer;
//
// Setting the calendar and the today date
//
Date today(2018, JUN, 20);
PLNHoliday holiday;
.addHoliday(holiday)
.withSpotLag(2);
//
// Reading the command line arguments; If not provided, program uses default names
//
auto data_file = args.first.empty() ? "../data/curve_data.csv" : args.first;
auto settings_file = args.second.empty() ? "../data/curve_settings.csv" : args.second;
//
// Creating benchmark instruments
//
SHOW(df_instruments);
std::vector<Deposit> deposits = ir::readDeposit(df_depo, today, calendar);
std::vector<FRA> fras = ir::readFRA(df_fra, today, calendar);
std::vector<IRS> swaps = ir::readIRS(df_irs, today, calendar);
std::vector<SmartPointer<ir::BuildingBlock> > benchmarks;
benchmarks.insert(benchmarks.end(), deposits.begin(), deposits.end());
benchmarks.insert(benchmarks.end(), fras.begin(), fras.end());
benchmarks.insert(benchmarks.end(), swaps.begin(), swaps.end());
//
// Reading curve settings
//
df_settings = df_settings.filter("Estimator",[](std::string x)->bool{return x == "unconstrained";} );
SHOW(df_settings);
//
// Constructing the curve
//
DataFrame estimation_resuts;
DataFrame calibration_results;
auto set_name = df_settings("Id", r);
SmartPointer<ir::SmootherCostFunction> scf = df_settings.getObject<ir::SmootherCostFunction>("SmoothingInput",r);
scf = ir::FirstDerivativeCostFunction(scf);
}
scf = ir::SecondDerivativeCostFunction(scf);
}
InterestRate rate(compounding, yf);
ir::CompoundedInterpolator interpolator(interpolation, inputs);
.asOfDate(today)
.withCalendar(calendar)
.withInterestRate(rate)
.withInterpolator(interpolator)
.withSetOfInstruments(benchmarks)
.usingEstimator(estimator);
calibration_results.append(calib);
estimation_resuts.append(curve_data);
//
// Print one curve as example
//
if (set_name == "Set30") {
SHOW(curve);
}
}
//
// Saving results
//
estimation_resuts.printToCsv("unconstrained_results");
}


 1.8.11
1.8.11