Class implements interface for differential schemes. More...
#include <fdScheme.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual void | setSolver (const SmartPointer< TridiagonalSolver > &solver)=0 |
| Provides a solver used in implicit scheme. | |
| virtual std::vector< double > | solve (std::vector< double > f, const std::vector< SmartPointer< BoundaryCondition > > &bcs, const std::vector< double > &time_grid, const TridiagonalOperator &L)=0 |
| Solves PDE defined by provided linear operator L and initial and boundary conditions. More... | |
| virtual std::vector< double > | solveAndSave (std::vector< double > f, const std::vector< SmartPointer< BoundaryCondition > > &bcs, const std::vector< double > &spatial_grid, const std::vector< double > &time_grid, const TridiagonalOperator &L, const std::string file_name)=0 |
| Solves PDE defined by provided linear operator L and initial and boundary conditions. Additionally saves solution to CSV file. More... | |
| virtual std::string | info () const =0 |
| Returns scheme name. | |
| virtual FDScheme * | clone () const =0 |
| Virtual copy constructor. | |
| virtual | ~FDScheme () |
| Deconstructor. | |
Detailed Description
When we solve following parabolic PDE:
![\[\frac{df(x,t)}{dt} = L f(x,t)\]](form_19.png)
where L is linear operator, we can use different time discretization scheme, for example in case of Forward Kolmogorov Equation:
![\[ \begin{aligned} \text{in case of explicit scheme: }\frac{f(x_i,t_{j+1})-f(x_i,t_{j})}{t_{j+1}-t_{j}} & = \hat{L} f(x_i,t_{j}) \Rightarrow f(x_i,t_{j+1})= (I + (t_{j+1}-t_{j})\hat{L}) f(x_i,t_{j}) \\ \text{in case of explicit scheme: }\frac{f(x_i,t_{j+1})-f(x_i,t_{j})}{t_{j+1}-t_{j}} & = \hat{L} f(x_i,t_{j+1}) \Rightarrow f(x_i,t_{j})= (I - (t_{j+1}-t_{j})\hat{L}) f(x_i,t_{j+1}) \end{aligned} \]](form_21.png)
The difference between implicit scheme and explicit scheme lies in number of unknown values of on the time level. In explicit scheme we have three known values (in case of forward equation): 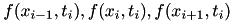 and one unknown
and one unknown 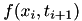 . This is why we can explicitly find the unknown values. In case of implicit we have three unknown values and one known for each time point. Solving this kind of system requires finding global solution. Because of that implicit scheme is numerically more demanding, but it is unconditionally stable in contrast to explicit scheme. For more information see [2] [5] [10] .
. This is why we can explicitly find the unknown values. In case of implicit we have three unknown values and one known for each time point. Solving this kind of system requires finding global solution. Because of that implicit scheme is numerically more demanding, but it is unconditionally stable in contrast to explicit scheme. For more information see [2] [5] [10] .
Member Function Documentation
|
pure virtual |
- Parameters
-
f Initial condition bcs Boundary conditions time_grid Time grid used in L Linear operator defining PDE
- Returns
- Solution in form of std::vector
Implemented in marian::ExplicitScheme, marian::ImplicitScheme, and marian::CrankNicolsonScheme.
|
pure virtual |
- Parameters
-
f Initial condition bcs Boundary conditions spatial_grid Spatial grid corresponding to initial conditions (used only to save the solution to CSV file) time_grid Time grid used for time dimension of FDM L Linear operator defining PDE file_name Name of CSV file
- Returns
- Solution in form of std::vector
Implemented in marian::ExplicitScheme, marian::ImplicitScheme, and marian::CrankNicolsonScheme.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- C:/Unix/home/OEM/fdm/src/FDM/schemes/fdScheme.hpp


 1.8.11
1.8.11